Question 1
Explanation
At the end of each frame there is a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field. FCS can be analyzed to determine if errors have occurred. FCS uses cyclic redundancy check (CRC) algorithm to detect errors in the transmitted frames. Before sending data, the sending host generates a CRC based on the header and data of that frame. When this frame arrives, the receiving host uses the same algorithm to generate its own CRC and compare them. If they do not match then a CRC error will occur. CRC errors (and input errors in general) are often caused by duplex mismatch or Physical layer issues (like faulty cable, faulty network interface card or excessive interference during the transmission,…).
On an Ethernet connection, a duplex mismatch is a condition where two connected devices operate in different duplex modes, that is, one operates in half duplex while the other one operates in full duplex.
Note:
+ Runts are frames which do not meet the minimum frame size of 64 bytes. Runts are usually created by collisions.
+ Giants: frames that are larger than 1,518 bytes
Question 2
Explanation
The ports on the switch are not up indicating it is a layer 1 (physical) problem so we should check cable type, power and how they are plugged in.
Question 3
Question 4
Question 5
Question 6
Explanation
The “show ip nat statistics” only gives us information about NAT translation. We cannot know if IP routing is enabled or the VLANs are up not not.
The “show ip statistics” command does not exist.
With the “show ip interface brief” we can see if the interface VLANs are up or not but cannot see if IP routing is enabled or not. So let’s see what information can be learned with the “show ip route” command.
By using the command “show ip route” we will learn if IP routing is enabled. If it is not enabled we will see this output:
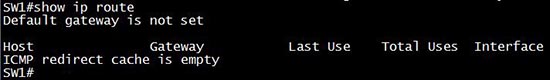
After enabling ip routing (via the “ip routing” in global configuration mode) we can see all the interfaces. For example:
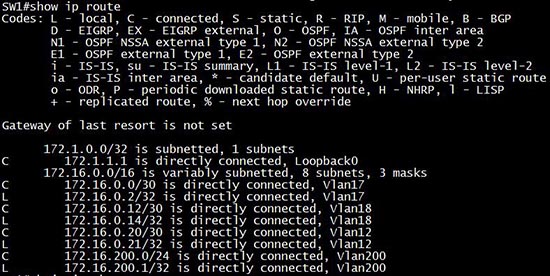
If we shut down an interface VLAN (Vlan18)
Sw1(config)#interface vlan 18
Sw1(config-if)#shutdown
then we will not see it in the routing table any more.
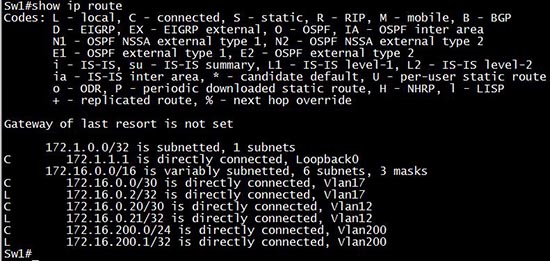
Therefore if the statement “local VLANs are up” means “the interface VLANs are up” then the “show ip route” is the best answer in this case.
Note: The IOS used to test is IOSv15.1